What to See in England
By Gordon Home
Pevensey Castle
LANDING-PLACE OF WILLIAM THE CONQUEROR
=How to get there.=–Train from London Bridge or Victoria. London, Brighton, and South Coast Railway. =Nearest Station.=–Pevensey and West Ham. =Distance from London.=–65 miles. =Average Time.=–Varies between 2 and 3 hours.
1st 2nd 3rd
=Fares.=–Single 10s. 0d. 6s. 2d. 4s. 8d.
Return 17s. 6d. 11s. 8d. 9s. 4d.
=Accommodation Obtainable.=–"Royal Oak Inn” at Pevensey village.
Pevensey, the scene of so many notable events in English history, was probably a fishing-port in prehistoric times. It is situated on flat and low-lying marsh-land, about 15 miles westward along the coast from Hastings. Here the Romans built a town and fortress. Entering Pevensey Castle by the main gateway, you stand on the site of the Roman city of Anderida, of which many evidences remain in the shape of Roman cement and tiles in a wall which surrounds the enclosure. The Romans retired from Anderida in the fifth century, when it was destroyed by the Saxons under Ella, and the inhabitants slain for their obstinate resistance.
A fortnight before the great battle on Senlac Hill, William of Normandy landed at the old Roman city. After the Conquest, Roger, Earl of Mortmain and Cornwall, half-brother of the Conqueror, built the Norman building whose shattered walls are to be seen to-day. William Rufus, Simon de Montfort, and Stephen each attacked the castle, and it remained a fortress until the reign of Queen Elizabeth. In the south-eastern corner of the Brito-Roman city, there still stands an interesting old culverin, bearing the crown, Tudor rose, and the initials of Queen Elizabeth. It is one of two cannon placed there in 1587 in readiness for the Spaniards. The present castle shows the different work of several centuries. The remains of a much-weathered stone font, surrounded by an iron cage, stand in the centre of the enclosure. Near by, within a palisade, is the old castle well, with hart’s-tongue ferns growing on the damp brick lining.
At one time Pevensey formed, with Hastings, one of the Cinque Ports. It began to decline as a seafaring place with the loss of its harbour, owing to the receding of the sea along the Sussex shore–the walls, which were formerly almost washed by the waves, being now quite a mile inland. Visitors may enter the castle on week days without charge.
[Illustration: PEVENSEY CASTLE.
Before the sea receded the waves almost reached the Castle walls.]
WINCHESTER & ITS CATHEDRAL
=How to get there.=–Train from Waterloo. L. and S.W. Railway. =Nearest Station.=–Winchester. =Distance from London.=–66-1/2 miles. =Average Time.=–Varies between 1-1/2 to 2-3/4 hours.
1st 2nd 3rd
=Fares.=–Single 11s. 0d. 7s. 0d. 5s. 6d.
Return 19s. 3d. 12s. 2d. 10s. 6d.
=Accommodation Obtainable.=–"George Hotel,” “Royal Hotel," “Black Swan Hotel,” etc. =Alternative Route.=–Train from Paddington. Great Western Rly.
Winchester, the ancient Saxon capital of England, is situated near the foot of the chalk uplands surrounding the river Itchin. It is a city full of historical interest, and its two most striking features are the cathedral and college. Long before the Norman Conquest there was a grammar school at Winchester under the care of the monks. Bishop William of Wykeham was educated at this earlier school, and it was he who re-established it on a larger scale. The new college was founded at the end of the fourteenth century, under the direction of a corporation, and was allied to one of the colleges at Oxford. For five centuries this college, the most ancient of the public schools in England, has kept a foremost place among the many educational centres that now exist. Many of the college buildings remain almost the same as they were originally founded.
The cathedral, which is the largest in England, shows every style of architecture from pure Norman to Early Renaissance. It was founded by Walkelin, the first Norman bishop, whose carved font is one of the finest treasures of the building. Bishop Wykeham, at the end of the fourteenth century, continued the building, which had been steadily progressing for a considerable time, and commenced the partial casing of the Norman columns with Perpendicular mouldings. The vaulting shafts of the nave rise from the ground, and owing to the thickness of the Norman masonry, there is no proper triforium. The reredos was built by Cardinal Beaufort in the fifteenth century, and the Lady Chapel was added about the same time. Though it suffered much damage during the Parliamentary wars, the cathedral is wonderfully rich in monuments, all its various architects being buried there, and among the many shrines is that of William Rufus.
Winchester’s associations with King Alfred, and its numerous examples of architecture of all the centuries, make the city one of the most interesting in England.
[Illustration: Photochrom Co., Ltd. WINCHESTER CATHEDRAL.
Showing the Norman north transept and the west end.]
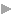 Continue...
Continue...![[Buy at Amazon]](http://images.amazon.com/images/P/B0006ADKOC.01.MZZZZZZZ.jpg)